In an increasingly connected world, the need for robust security measures has become paramount. Traditional methods such as passwords and PINs, once considered foolproof, are no longer sufficient to protect our sensitive data. As technology continues to advance, biometric security offers a compelling alternative that goes beyond conventional authentication methods.
What is Biometric Security?
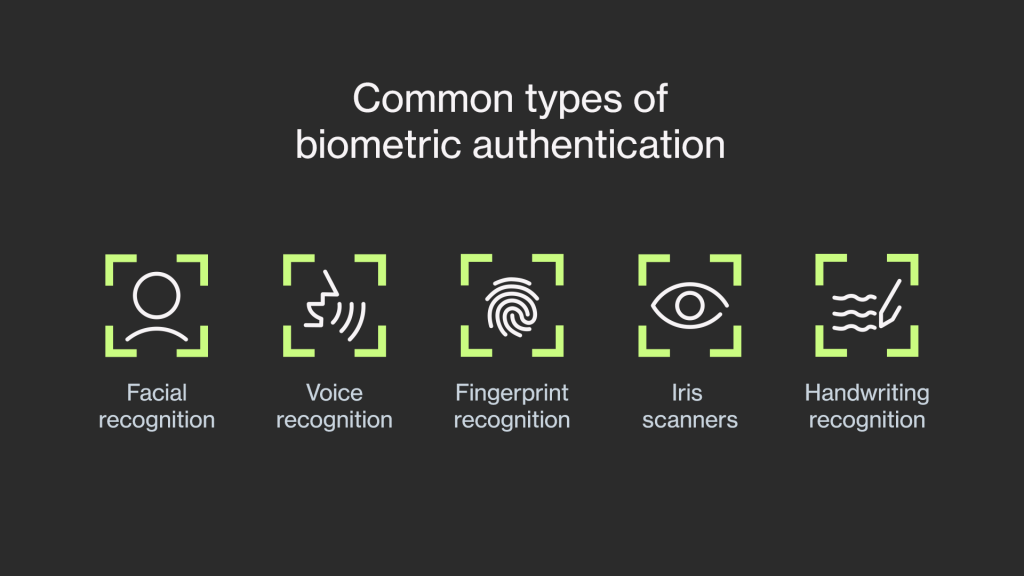
Biometric security is a technology that uses unique biological characteristics to authenticate individuals and grant access to systems or devices. These characteristics include fingerprints, iris and retina patterns, facial features, voice recognition, and even behavioral traits like typing rhythm.
Advantages of Biometric Security
1. Enhanced Security
Unlike traditional passwords and PINs, biometric security measures are nearly impossible to replicate or guess. Each person’s biometric features are unique, making it significantly more challenging for hackers to gain unauthorized access.
2. Convenience
Biometric authentication eliminates the need to remember and frequently change passwords or carry physical tokens. Users can simply utilize their own unique physiological or behavioral traits for seamless and hassle-free access.
3. Speed and Efficiency
Biometric identification can be carried out within seconds, reducing the time required for authentication. This makes it ideal for scenarios where quick access is essential, such as unlocking mobile devices or authorizing transactions.
4. Versatility
Biometric security can be deployed across various platforms and devices, including smartphones, laptops, access control systems, and even vehicles. This versatility allows for a seamless user experience across different environments.
Applications of Biometric Security
The adoption of biometric security has seen tremendous growth across different industries. Here are some prominent applications:
1. Mobile Devices
Smartphones and tablets now commonly utilize fingerprint scanners or facial recognition technology to unlock devices and authorize payments. This offers users a seamless and secure experience, making it difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access.
2. Financial Services
Banks and financial institutions are increasingly adopting biometric security to enhance their authentication processes. By implementing technologies such as iris scans or voice recognition for transactions, they can provide an additional layer of security and prevent fraud.
3. Healthcare
Biometric security plays a vital role in the healthcare sector by ensuring secure access to patient records and sensitive medical information. This technology offers doctors and other healthcare professionals quick and reliable identification methods to protect patient privacy.
4. Travel and Border Control
Airports and border control agencies worldwide have implemented biometric security systems to effectively manage and secure border crossings. Technologies such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning enable faster processing, while simultaneously improving safety and reducing identity fraud.
Future of Biometric Security
As technology evolves, biometric security is poised to play an even more significant role in safeguarding our digital and physical lives. Innovations like palm vein recognition and gait analysis offer new possibilities for authentication and access control, further enhancing security measures.
However, despite the myriad of advantages, it is essential to address concerns related to privacy and the potential misuse of biometric data. Striking the right balance between convenience and security, while respecting individuals’ privacy rights, will be crucial as biometric security continues to advance.
In conclusion, biometric security surpasses the limitations of traditional authentication methods, proving to be a reliable, convenient, and secure approach. As it gains wider acceptance, biometrics will reshape how we safeguard our digital identities, offering a technologically advanced alternative to passwords and PINs.